A black plastic 3.5 inch diameter grenade.
The British No. 69 was a hand grenade developed and used during the Second World War. It was adopted into service due to the need for a grenade with smaller destructive radius than the No. 36M “Mills bomb”. This allowed the thrower to use a grenade even when there was little in the way of defensive cover. In contrast, the much greater destructive radius of the Mills bomb than its throwing range forced users to choose their throwing point carefully, in order to ensure that they would not be wounded by the shrapnel explosion of their own grenade.
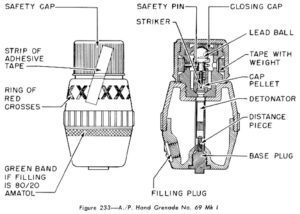
The shell of the No. 69 grenade was composed entirely of the hard plastic, Bakelite, which shattered without producing fragments like a metal bodied grenade. Metal fragmenting sleeves were available to increase the grenade’s lethality.
Using the No. 69 bomb was very simple: the screw-off cap was removed and discarded, and the grenade was then thrown. When the grenade was thrown, a linen tape with a curved lead weight on the end automatically unwrapped in flight, freeing a ball-bearing inside the fuze. In this manner the “all ways” action impact fuze was armed in flight and the grenade exploded on impact; and like the Gammon grenade, which used the same fuze design, it was withdrawn from service soon after the Second World War ended.